Enter the order reference number received by email to check the status or make payment.
Powerful Protection from Payment to Delivery
Secure and Reliable Payment
Money Back Guarantee
Shipping and Delivery
After-Sales Service
Understanding the Function, Types, and Capacitance Range of Variable Capacitors
One type of primary capacitor is the variable capacitor. Capacitors are classified into two types based on their capacitance: fixed capacitors and variable capacitors. Fixed capacitors have a fixed capacitance value, while variable capacitors have the ability to change their capacitance values either electrically or mechanically.
Unlike fixed capacitors, variable capacitors offer specific ranges of values instead of predetermined values during manufacturing. The choice of variable capacitors depends on the desired capacitance values. These capacitors are commonly used in tuning circuits.
1. What is a Variable Capacitor?
A variable capacitor, also known as a variable capacitor, is a type of capacitor that allows for the adjustment of its capacitance within a specific range as needed.
These capacitors are constructed using metal plates, with one plate fixed in place and the other plate movable.
The capacitance range of variable capacitors typically ranges from 10 picofarads to 500 picofarads.
They are also referred to as "ganged capacitors" because they can be interconnected, allowing for multiple variable capacitors to be controlled by a single shaft.
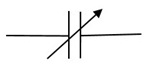
The symbol used to represent a variable capacitor is simple and clear, featuring an arrow to indicate its variable nature.
2. Construction of Variable Capacitor
The variable capacitor's construction is shown below. These capacitors are commonly used in various applications due to their simple construction. They are typically made up of two sets of hemispherical metal plates that are separated by air gaps. One set of plates is fixed, while the other set is connected to a shaft, allowing the user to rotate the assembly and adjust the capacitance as needed. The construction of each type of capacitor can vary.
The working principle of a basic capacitor is applied to design this variable capacitor. The conductive plates of the capacitor are arranged in parallel and separated by dielectric coatings made of materials such as reinforced paper, mica, or certain types of ceramics. Unlike traditional fixed capacitors, these capacitors are designed to change capacitance levels. This is achieved by adjusting the distance between the parallel plates within the capacitor.

- The capacitor is constructed by inserting metal plates into it.
- Some of the plates are fixed, while the others are movable.
- The capacitance changes as a result of rotating the movable plates, which alters the area between the fixed and movable plates.
- Each type of capacitor in this category has a unique construction.
3. Types of Variable Capacitors
In the market, there are two types of variable capacitors: tuning capacitors and trimmer capacitors. These capacitors allow for manual adjustment of capacitance using screwdrivers or other devices.
3.1 Tuning Capacitors:
Tuning capacitors are designed with a frame that consists of a stator and a rotor. The stator supports the mica material and the rotor. When the stator is turned, the rotor plates rotate with the help of a shaft. The capacitance value of these capacitors is maximum when the movable rotor plates enter the immobile stator, and minimum when they are apart. Tuning capacitors can provide capacitance values ranging from picofarads to tens of picofarads. They are commonly used in radio receivers with LC circuits and are also known as tuning condensers.
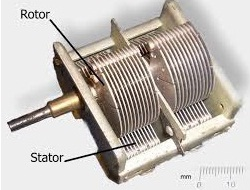
3.2 Common problems in tuning circuits:
Variable capacitors used in tuning circuits can encounter several issues. One common problem is a bend in the plates, which can cause a short circuit and render the component inoperative. It is important to check for any indication of low resistances around the entire turn of the variable capacitor. In good condition, the meter's needle should remain on infinite. If a short is detected between the plates, the first step is to attempt to correct the alignment of the plates using the screw on the mobile variable axis. The plates can be adjusted by pressing and releasing this screw if they are bent. The technician should carefully correct the defect, continuously testing for continuity to determine when the component is recovered. Insulating sheets inside the capacitor may also contribute to a small short circuit problem. By dismantling the component and examining the defective sheets, the technician can attempt to correct the defect. Alternatively, other abandoned variables with insulating sheets can be used, or insulating sheets can be improvised. After reassembly, an isolation test should be conducted to ensure that the short circuit between the plates has been eliminated. If the problem is caused by moisture or dirt, the variable can be disassembled for cleaning, taking care not to bend the plates, and ensuring that any insulating sheets are reassembled.
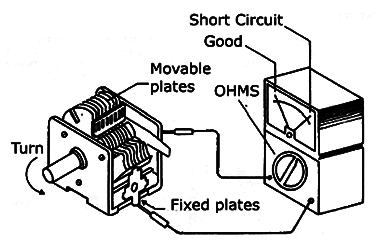
Testing a variable capacitor with a multimeter.
3.3 Trimmer Capacitors:
Trimmer capacitors are used for basic calibration of equipment during manufacturing or servicing. These capacitors are often arranged on the printed circuit board in such a way that the user does not have access to change them. As a result, they are inexpensive. Trimmer capacitors are used in circuits to set the oscillator frequency, rise and fall times, and latencies. They allow servicemen to adjust devices as needed. Trimmer capacitors can be classified into two types: air trimmer and ceramic trimmer. They have three leads: one connected to the immobile part, one to the rotary part, and one to the common part. The movement of the capacitor is observed through a semi-circle-shaped movable disc. Trimmer capacitors consist of two plates separated by a dielectric material arranged in parallel.

3.4 Mechanical Capacitors:
Mechanical capacitors consist of a series of curved plates connected to a knob. The advantage of these capacitors is that their capacitance can be easily changed if necessary. They are mechanically reliable due to their simple design.
3.5 Electronic Capacitors:
Electronic capacitors have their capacitance changed by applying a DC voltage. These capacitors are commonly used in multimeters to measure resistance and amperage. The term "DC" refers to the type of current supplied by a battery.
4. Working principle of Variable Capacitors
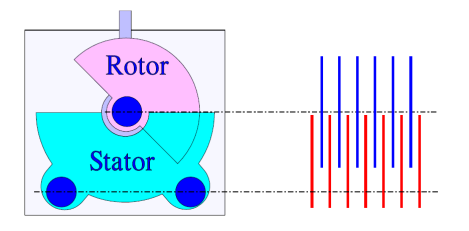
The capacitance can be adjusted within a range of values by using an electrode system consisting of a fixed part called the stator and a movable part called the rotor.
The temperature coefficient (TC) for different dielectrics varies significantly compared to fixed capacitors. Except for high-precision components, the variations are generally larger due to mechanical conditions and overall construction.
Trimmer capacitors are mainly used in printed circuit boards (PCBs), but surface mount designs are becoming increasingly popular. Trimmers often have friction, which increases the turning force and locks the capacitor in its adjusted position.
4.1 Types of variable capacitors
Air dielectric: As shown in Figure, the classic variable capacitor consists of semicircular electrodes that can be rotated towards each other. These designs are suitable for both PCB and panel mounting and are commonly used for tuning resonance circuits.
Mechanical precision is required due to the air-insulated electrodes. The plate distance is typically between 0.2 and 1 mm, making the cost relatively high.
4.2 Ceramic trimmers:
A ceramic trimmer capacitor can be created by reducing the number of plates in Figure to a single silver-plated ceramic rotor that is rotated over the stator electrode. There are also multilayer designs available. These capacitors can be mounted through holes or on the surface of PCBs. The use of Type 1 ceramics ensures minimal losses.
4.3 Plastic foil types:
By replacing the air insulation in Figure with plastic foil, the electrode distance can be reduced, resulting in an increased capacitance (denoted as r). However, this comes at the expense of a slightly lower Q value. Common low-loss plastics used include Teflon (PTFE), polypropylene (PP), polycarbonate (PC), and polyester (PETP).
5. Variable Capacitor Applications
The variable capacitor finds its applications in various fields, including the following:
1. Trimmer capacitors: These capacitors are used in the manufacturing process when a specific capacitance value needs to be matched to a particular circuit. They are particularly useful when the components in a circuit have different tolerances. By using trimmer capacitors, the tolerance values in a circuit can be adjusted to match the desired specifications, even if they deviate by up to 20% from the original design.
2. Microwave circuits: Variable capacitors, including trimmer capacitors, are frequently employed in microwave circuits. These circuits require precise tuning and adjustment to achieve optimal performance, and variable capacitors allow for fine-tuning of the circuit's characteristics.
3. Medical instruments: Variable capacitors are utilized in medical instruments such as NMR scanners and MRI machines. These instruments require the generation of extremely high magnetic fields, and variable capacitors play a crucial role in achieving the necessary magnetic field strength.
4. Tuners, oscillators, filters, and crystal oscillators: Variable capacitors are commonly used in these types of circuits to adjust the frequency response and resonance characteristics. They enable precise tuning and frequency control, ensuring optimal performance in these applications.
5. Communication devices: Variable capacitors, including trimmer capacitors, can be found in various communication devices. These include mobile radios, aerospace transmitters and receivers, CATV amplifiers, and signal splitters. Variable capacitors allow for precise adjustment of the circuit's characteristics, ensuring reliable and efficient communication.
6. FAQ
1) What is the main function of the variable capacitor?
The main function of a variable capacitor is to adjust or fix the resonant frequency in an LC circuit. By changing the capacitance value, the resonant frequency can be tuned to a desired frequency.
2) How are these capacitors made?
Variable capacitors are typically made using two sets of curved metal plates that are separated by air gaps. The plates can be rotated or moved closer together or farther apart to change the effective capacitance.
3) What is a ganged capacitor?
A ganged capacitor refers to the combination of two or more capacitors that are connected together. This allows them to be adjusted simultaneously, making it easier to tune multiple circuits or sections of a circuit.
4) What are the two types of variable capacitors?
The two main types of variable capacitors are tuning capacitors and trimming capacitors. Tuning capacitors are designed to adjust the resonant frequency in a circuit, while trimming capacitors are used during the manufacturing process to fine-tune the capacitance value and match the desired circuit specifications.
5) What is the typical range of capacitance values for a variable capacitor?
Variable capacitors typically have a capacitance range of 100pF to 500pF. However, the actual range can vary depending on the specific application and design requirements.
Recent Posts








Company
About UsContact UsTerms & ConditionsPrivacy StatementPayment,Shipping & InvoiceRefund & Return PolicyWarranty PolicyFrequently asked questionHolidays for Chinese Mid-Autumn Festival and National Day in 2023
 US
US
















