Enter the order reference number received by email to check the status or make payment.
Powerful Protection from Payment to Delivery
Secure and Reliable Payment
Money Back Guarantee
Shipping and Delivery
After-Sales Service
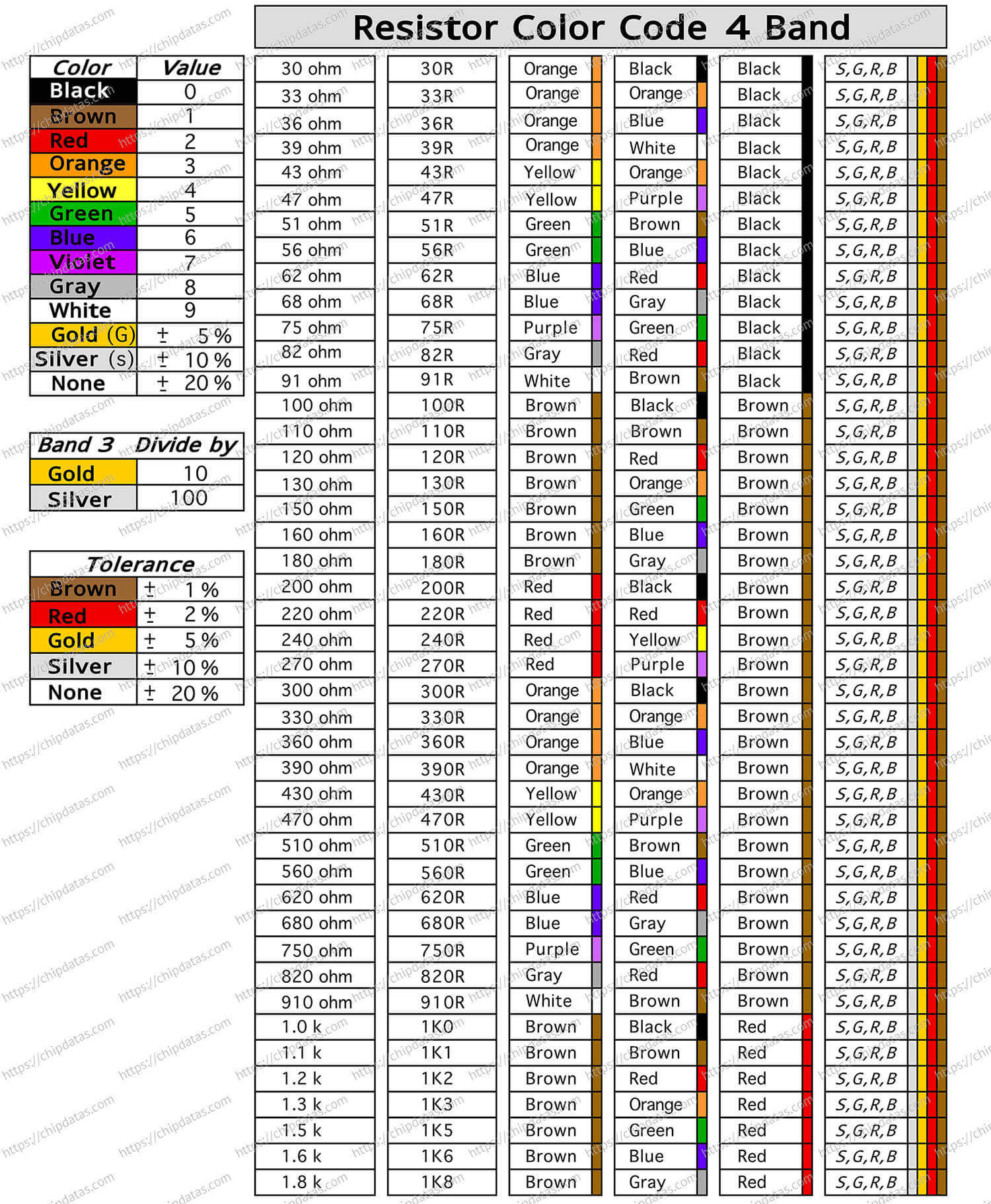
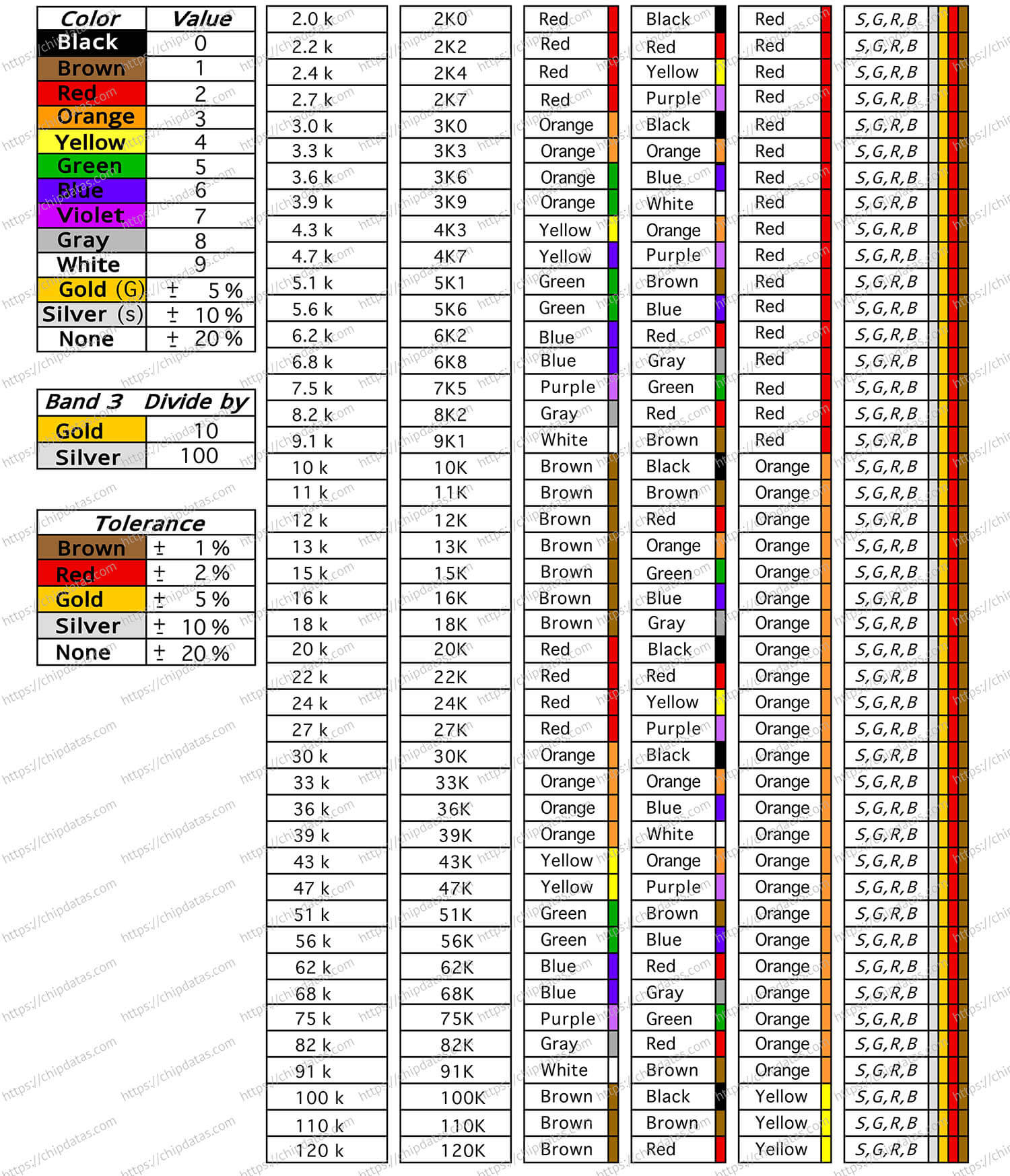
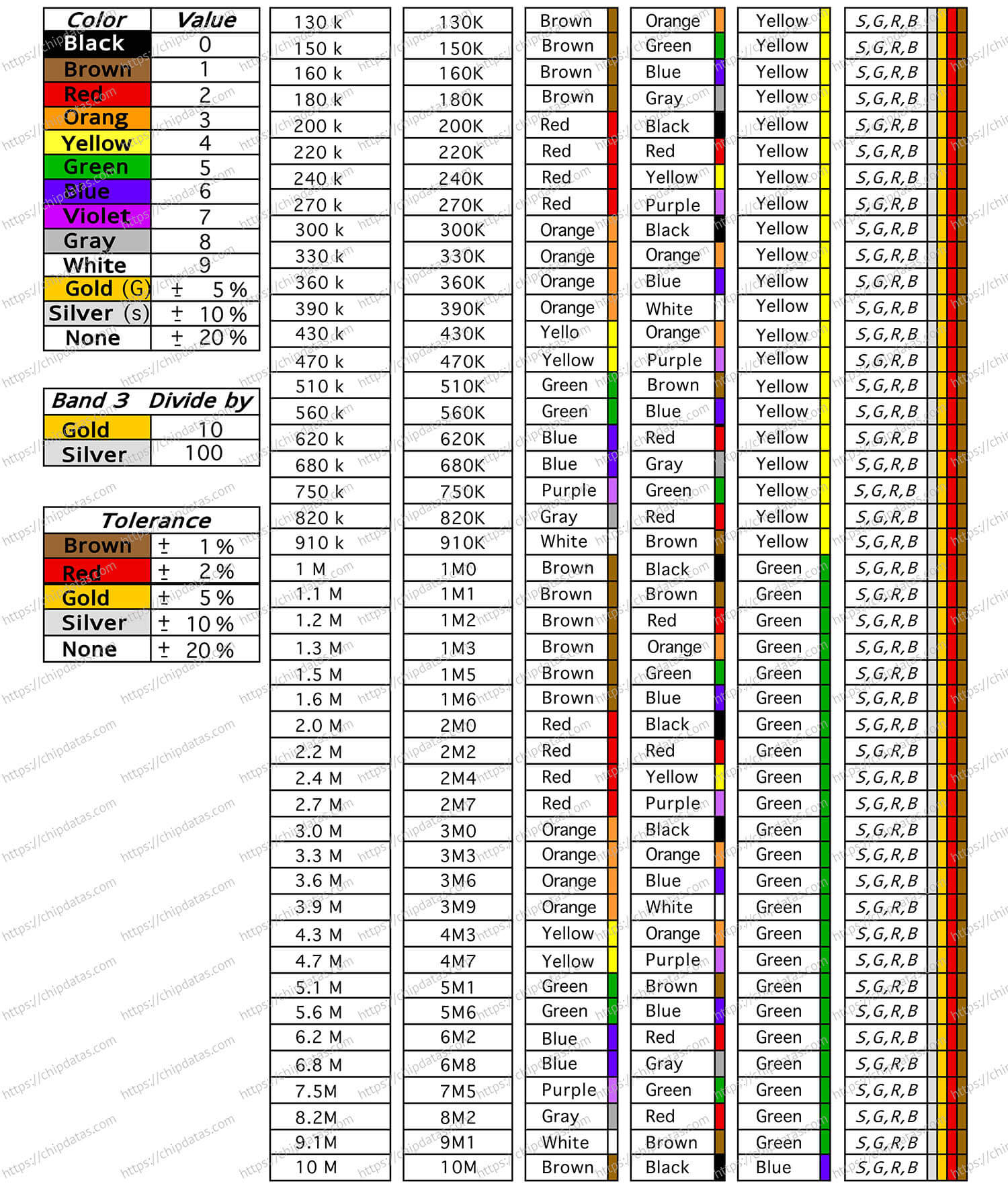
Resistor color code chart for beginners
Basic information on resistors for beginners in electronics is found on this page, including the History of resistors、Four-band resistor color coding rules and Resistor color code chart.
Resistors are common electronic components that provide resistance in circuits, thereby controlling the current, adjusting the signal amplitude, dividing the voltage, biasing active elements, terminating transmission lines and so on. Resistors are one of the earliest electrical attributes discovered, almost at the same time as the discovery of electric current. Different materials have different resistance properties, for example, copper, aluminum and gold are considered good conductors (low resistance), stainless steel, carbon, tungsten are considered medium conductors (medium resistance), and ceramics, mica and air are considered poor conductors (high resistance). Ohm’s law defines the relationship between circuit attributes: Resistance = Voltage / Current Resistance = Power / ( Current^2 ) In addition to the ohmic attribute, resistance can also be defined as a function of noise voltage, as part of Noise Power = kTBf, where a resistor above absolute zero temperature is a source of noise. When a resistor is combined with a capacitor or an inductor, the current through this network will be out of phase with the applied voltage, and called displacement current. The combination of resistance with capacitance / inductance is known as impedance, and complex mathematics is used to build on the basic ohm’s law shown above.
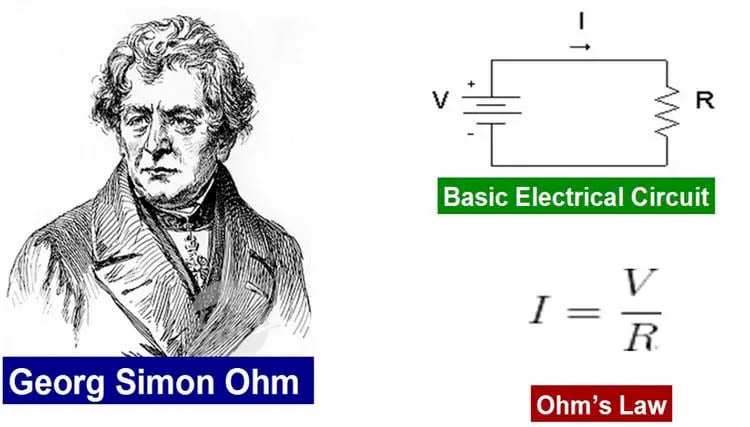
History of resistors
According to some sources , we can learn some facts about the history of resistors:
- In 1827, Georg Simon Ohm invented the resistor at the University of Erlangen. Ohm was a mathematician who published many research papers on heat conduction in molded circuits and presented the ohm’s law.
- In 1872, ohm was determined as the unit of measuring resistance.
- In 1893, the first carbon film fixed resistor was exhibited at the Chicago World’s Fair.
- In 1906, Walter Schottky invented the metal film fixed resistor.
- In 1925, Otto Feist invented the metal foil fixed resistor.
- In the 1930s, variable and precision resistors began to appear.
- In 1961, Walter Boykin obtained a patent for improving the manufacturing method and structure of carbon film fixed resistors.
- Since the 1970s, with the development of surface mount technology and integrated technology, various types and specifications of resistors with smaller size and higher performance have appeared.
Four-band resistor color coding rules
Four-band resistors are common fixed-type carbon film resistors. They have four colored rings on their surface to indicate their resistance value and tolerance. For beginners, it is necessary to understand the meaning of these color rings, because they can help you choose the appropriate resistor or identify the parameters of the resistor in the circuit diagram. The color coding rules for four-band resistors are as follows:
- The first ring represents the first significant digit
- The second ring represents the second significant digit
- The third ring represents the multiplier, that is, the power of 10
- The fourth ring represents the tolerance, that is, the percentage deviation from the nominal value
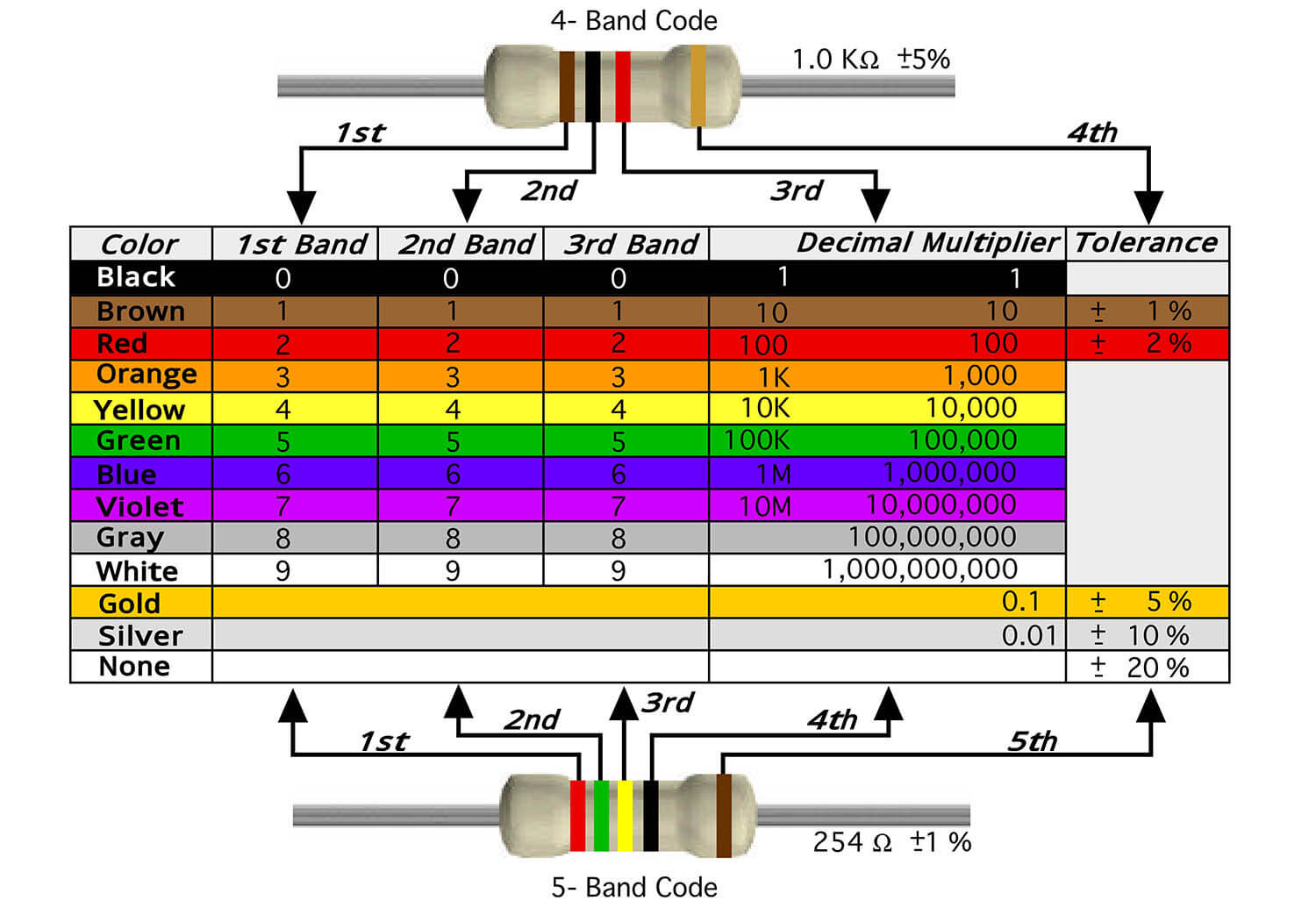
Different colors represent different numbers or multiples. For example, black represents 0, red represents 2, gold represents 0.1 times, silver represents 0.01 times and so on. Here is a color coding table that you can use to remember the meanings of different colors:
| Color | Number | Multiplier | Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Black | 0 | x10^0 | - |
| Brown | 1 | x10^1 | ±1% |
| Red | 2 | x10^2 | ±2% |
| Orange | 3 | x10^3 | - |
| Yellow | 4 | x10^4 | - |
| Green | 5 | x10^5 | ±0.5% |
| Blue | 6 | x10^6 | ±0.25% |
| Purple | 7 | x10^7 | ±0.1% |
| Gray | 8 | x10^8 | ±0.01% |
| White | 9 | x10^9 | - |
| Gold | - | x10^-1 | ±5% |
| Silver | - | x10^-2 | ±10% |
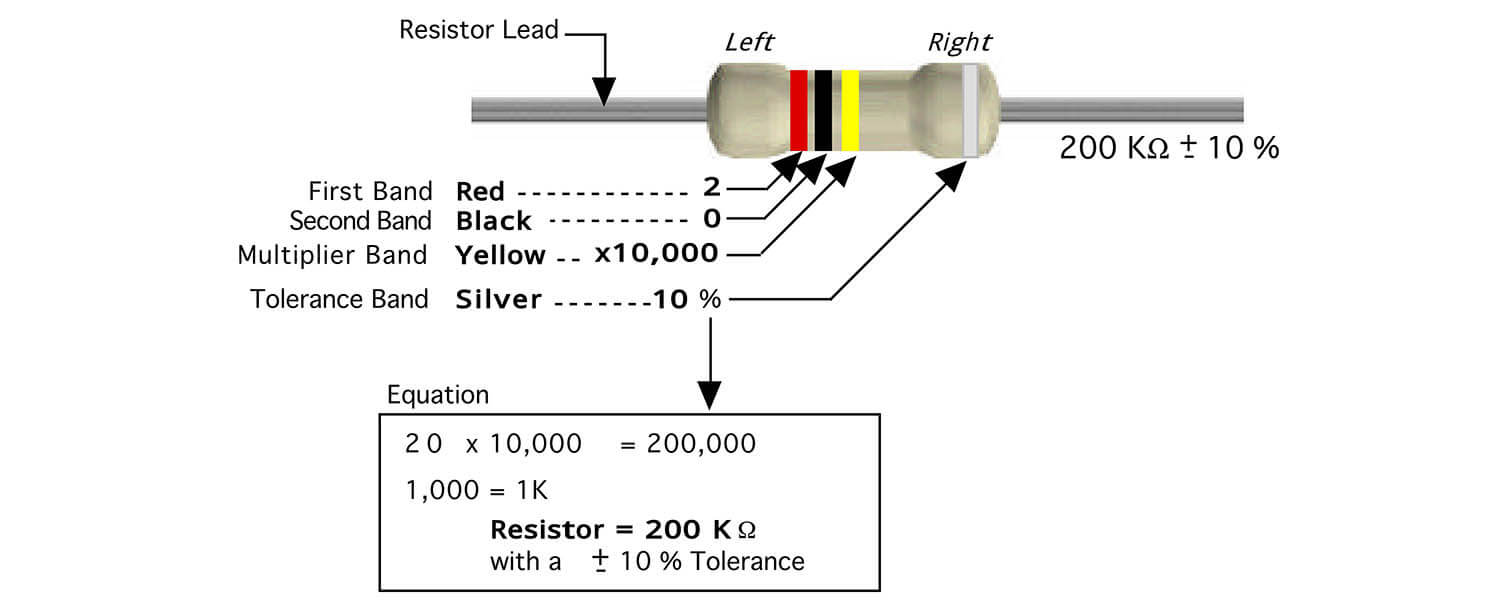
According to this table, you can use the following formula to calculate the resistance value and tolerance of four-band resistors:
Resistance = (First ring × 10 + Second ring) × Third ring × 10^(-2) Ω
Tolerance = ±(Fourth ring × Resistance)
For example:
a four-band resistor whose colors are red, purple, brown and gold has a resistance value of:
Resistance = (2×10+7)×10×10^(-2) Ω = 270 Ω
Tolerance = ±(0.05×270) Ω = ±13.5 Ω
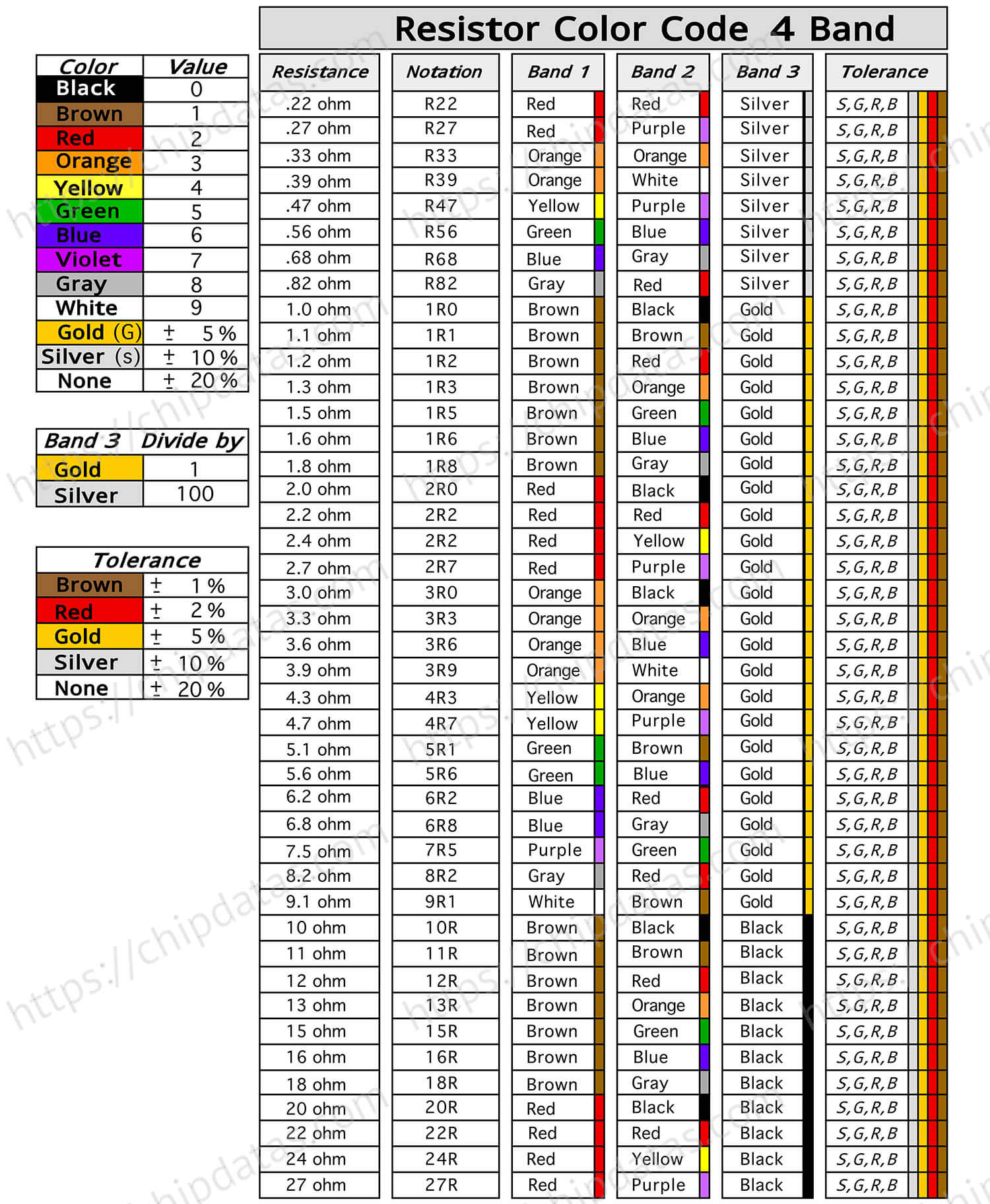
Here is an info sheet for a quick lookup of resistor values, symbols and tolerance values.
Summary
Resistors are important electronic components whose parameters are usually indicated by some coding methods. Beginners should master these coding methods in order to choose and identify suitable resistors in practical applications. This article introduces the history of resistors, then takes four-band resistors as an example to introduce their color coding rules, and finally give an information table “quickly query the resistance value, tolerance and temperature coefficient of four-band resistors”.
References
Recent Posts








Company
About UsContact UsTerms & ConditionsPrivacy StatementPayment,Shipping & InvoiceRefund & Return PolicyWarranty PolicyFrequently asked questionHolidays for Chinese Mid-Autumn Festival and National Day in 2023
 US
US
















