Powerful Protection from Payment to Delivery
Secure and Reliable Payment
Money Back Guarantee
Shipping and Delivery
After-Sales Service
How to make a better car fuse and related knowledge
Automotive fuses play a crucial role in safeguarding vehicle wiring and electrical equipment. These fuses are usually rated for circuits with a maximum direct current of 32 volts, although some types can handle 42-volt electrical systems. While they are primarily used in automobiles, they can also be found in non-automotive electrical products. These fuses are typically housed within the vehicle in one or more fuse boxes, also known as an integrated power module (IPM). These boxes are often located on one side of the engine compartment or under the dash near the steering wheel. In this article, we will discuss some important aspects of car fuses.
What is a car fuse?
Car fuses play a crucial role in safeguarding the electrical wiring of automobiles and trucks from overcurrent and short-circuiting. By disconnecting the circuit when a potentially dangerous level of current is detected, they prevent damage to the vehicle's electrical components. These fuses come in various types and sizes, each designed to suit specific applications and electrical equipment within the vehicle.
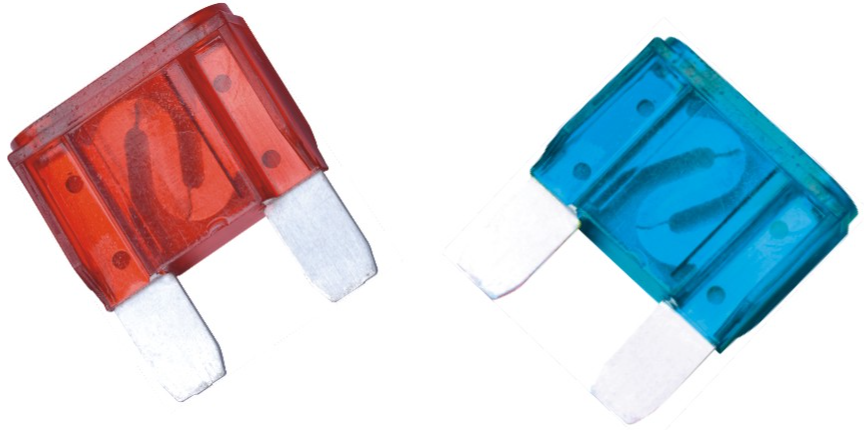
The majority of modern car fuses are blade-type fuses, identifiable by their colored plastic body and two prongs that fit into the socket. They can be installed in fuse blocks, fuse clips, or fuse holders, depending on the application.
How a Car Fuse Works?
A modern car's fuse box contains a range of multi-colored electrical fuses, along with larger plastic boxes called relays.
Fuses are installed on all of your car's electrical circuits to safeguard the components from any power surges. If the current flowing through the circuit exceeds a certain limit, the fuse will blow, interrupting the circuit and stopping the flow of electricity, thereby protecting the components further down the circuit.
Relays, on the other hand, are remote switches that allow an electrical circuit to be opened or closed. For instance, the headlight switch that turns your headlights on and off requires only a small amount of electricity. When you turn on the switch, instead of directly sending power to the headlights, it activates a relay, which in turn sends a large amount of power to the headlights.
Car Fuse Sizes
Here is a revised version of the article:
Automotive blade fuses come in six basic types, each with its own unique characteristics. Here is a breakdown of each type:
1. Micro2 – This is the smallest type of automotive blade fuse and is characterized by its tall, thin shape.
2. Micro3 – These fuses are easily identifiable because they are the only type with three terminals instead of two.
3. Low-profile mini – These fuses are small and compact, with terminals that do not protrude far from the main fuse body.
4. Mini – These fuses have the same body design as low-profile mini fuses but with longer terminals.
5. Regular – These are the most common type of automotive blade fuse and are the second-largest in size.
6. Maxi – The largest size available, maxi fuses are designed for high-current applications.
Types of Car Fuses
In order to determine the type of fuse used in your vehicle, you will most likely need to inspect the fuse box located inside the vehicle. Certain fuse types, on the other hand, are common to certain vehicles. The following are the most common fuse types found in automobiles.
1. Blade Type Fuses
If you own a car built after 1986, it most likely has blade fuses. The plastic body and two metal prongs of these fuses make them easily identifiable. Although nearly all gasoline-powered vehicles use a blade fuse, they are available in six different sizes with current ratings ranging from 1 amp to 100 amps.
2. Bosch Fuses
Bosch fuses are commonly found in older European vehicles. The conical ends and physical dimension size of 625mm distinguish a Bosch fuse. These fuses are also known as 6AC fuses, GBC fuses, and Torpedo fuses. The fuse's color indicates the ampere rating, which adheres to DIN 72581/1 standards. If you own a car from the 1980s or earlier, it may have a Bosch fuse.

3. Glass Tube Type Fuses
Up until 1986, a variety of tube type (cylindrical) glass fuses were commonly used in the manufacture of automobiles in the United States. The majority of these fuses were 1/4 inch in diameter but varied in length and were labeled with the AG suffix for 'automotive glass,' for example, 1AG, 3AG, 7AG, 8AG, SFE fuses, and so on. These glass fuses were typically available in 1A to 30A ratings.
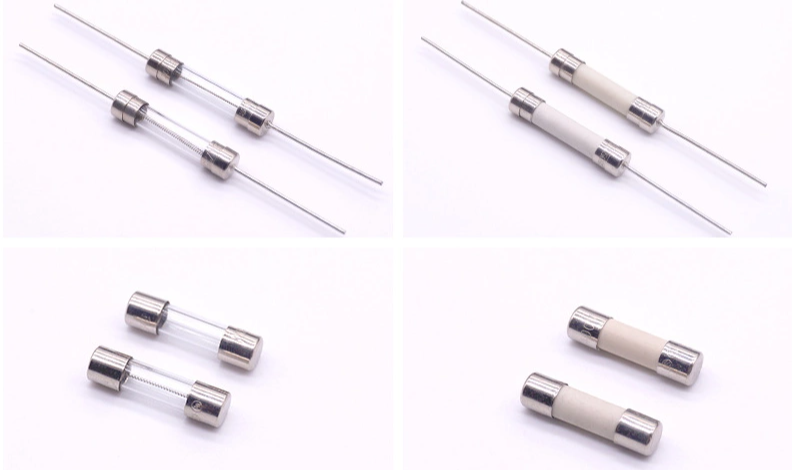

Glass Tube Fuses are still manufactured for a variety of different applications, despite the fact that they are no longer commonly used in vehicles. If you own a car manufactured in Northern America in 1986 or earlier, it may have a Glass Tube Type Fuse.
4. Lucas Fuses
Lucas Fuses are commonly found in older vehicles assembled or manufactured in the United Kingdom. Lucas Type Fuses are available in both ceramic and glass tube varieties. The ceramic fuse is easily distinguished by its canonical ends and measures 1 or 1.25 inches in length.
When compared to American Glass Tube Fuses, Lucas Glass Tube Fuses have different diameter sizes. Many Lucas Fuse Holders, however, can accommodate their American Glass Tube Fuse counterparts.
If you own a 1986 or earlier British model car, or a car assembled in Britain, and the fuse type is ceramic, you may need to look for a Lucas Fuse.

How to Inspect Car Fuses?
Car fuses are designed to be single-use and typically do not require regular maintenance unless they have blown. In most cases, a simple visual inspection can determine whether or not the fuse is in good working order. When a fuse blows or breaks, the wire is disconnected, and it is usually obvious that the continuous connection has been disrupted.
If a visual inspection is not possible or additional confirmation is needed, a multimeter can be used to check the fuse's status. There are two ways to do this:
1. Place the probes on either end of the fuse while the multimeter is in continuity mode. This allows the device to perform an electrical test and determine whether the fuse has continuity throughout. If the multimeter shows a high resistance or an error message (depending on the type of multimeter), the fuse is most likely blown and is not connected.
2. Use the multimeter's ohmmeter setting to check the fuse's resistance. Before taking this measurement, remember to remove the fuse from the fuse box or housing. Place the probes on both ends of the fuse and take the reading. A low reading, close to zero, usually indicates that the circuit is open and the fuse is working properly. A high reading and resistance value, on the other hand, indicates that the fuse has blown and there is a problem.
How to tell if a Car Fuse is blown?
If you suspect that a car fuse has blown, there are several simple steps you can take to confirm your suspicions. Start by identifying the fuse that controls the device that isn't functioning properly. You can typically find a diagram of the fuse box in the owner's manual, on the inside of the fuse box lid, or online. Once you've located the relevant fuse, use fuse pullers to remove it from the fuse box - but be sure to turn off your car completely beforehand. Check the fuse for any signs of discoloration or broken filaments. If you notice any damage, it's time to replace the fuse.
How to Replace a Car Fuse?
1. Locate Your Car Fuse
The location of the fuse box varies depending on the model and type of your vehicle. It's important to note that there may be multiple fuse boxes. Typically, cars have two fuse boxes: one under the hood and another beneath the dashboard near the steering wheel. To find the exact location of your fuse box, refer to your owner's manual. If you don't have one, a quick Google search can usually provide a free copy.
2. Remove a Car Fuse
Fuses can often be small and fragile, which can make removing them without causing damage to neighboring fuses a challenging task. Fortunately, many cars come equipped with a fuse puller, a handy device designed to simplify the process of removing automotive fuses. It is important to locate the fuse puller before attempting to remove a fuse, as it can assist in removing the affected fuse quickly and cleanly. In the event that your vehicle does not have a fuse puller, you can purchase one to effectively complete the task.
How to Change a Car Fuse Step by Step
Changing a blown automotive fuse is a simple process that can be done in a few easy steps. Follow these steps to learn how to change a fuse:
1. Locate the fuse panel in your vehicle. This can usually be found under the steering wheel or in the engine compartment. Consult your owner's manual if you're not sure where to find it.
2. Remove the cover from the fuse panel. Inside, you'll see a variety of colors and numbers denoting different amperages, as well as a diagram (usually on the reverse of the cover) indicating what each fuse powers in your vehicle.
3. Find the blown fuse. The interior is usually black, and the metal filament may be broken. If it's dark, use a flashlight to speed up the process.
4. Take out the blown fuse. To extract the blown fuse, use caution and a pair of pliers if necessary. Fuses can easily break, and a broken fuse is much more difficult to remove than a fully intact one.
5. Insert a replacement fuse of the appropriate amperage. Be sure to check the fuse panel and your owner's manual to ensure you're using the correct amperage. Using the wrong amperage fuse can lead to serious electrical problems.
6. Keep a few extra fuses of various amperages in your glove box in case of emergencies.
7. Start the engine to see if your hard work has paid off.
Remember, if the same fuse blows soon after you replace it, or if it doesn't work at all, it's time to call a mechanic.

Recent Posts








Company
About UsContact UsTerms & ConditionsPrivacy StatementPayment,Shipping & InvoiceRefund & Return PolicyWarranty PolicyFrequently asked questionHolidays for Chinese Mid-Autumn Festival and National Day in 2023