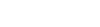Powerful Protection from Payment to Delivery
Secure and Reliable Payment
Money Back Guarantee
Shipping and Delivery
After-Sales Service
Enter the order reference number received by email to check the status or make payment.
Detailed Explanation of 10 Capacitance Classifications
Ceramic Capacitors (CC)
1. Structure
Ceramic capacitors use ceramic materials as dielectric, coated with a layer of metal (silver) film on the surface, and then formed as electrodes through high-temperature sintering. According to different dielectrics, ceramic capacitors can be divided into 1 type dielectric (such as NPO, CCG), 2 type dielectric (such as X7R, 2X1) and 3 type dielectric (such as Y5V, 2F4).
2. Characteristics
Type 1 ceramic capacitors have the advantages of low temperature coefficient, high stability, low loss, high voltage resistance, etc. The maximum capacity does not exceed 1,000 pF, and commonly used series include CC1, CC2, CC18A, CC11, CCG, etc. Type 2 and 3 ceramic capacitors have the characteristics of high dielectric constant, large capacity (up to 0.47 μF), small size, and inferior loss and insulation performance compared to type 1.
3. Applications
Type 1 ceramic capacitors are mainly used in high-frequency circuits. Type 2 and 3 ceramic capacitors are widely used in medium and low-frequency circuits, as capacitors for DC blocking, coupling, bypass, and filtering, etc. Commonly used series include CT1, CT2, CT3, etc.
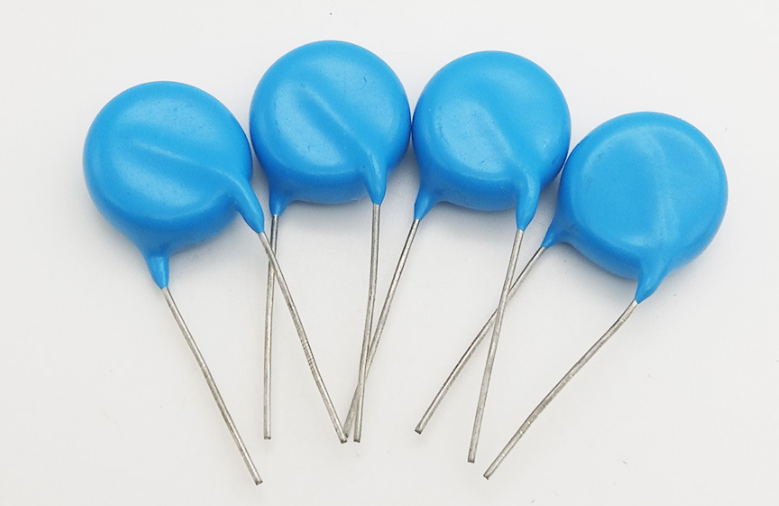

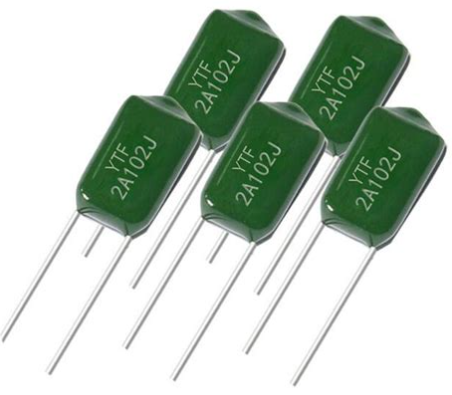
Polyester Capacitor (CL)
1. Structure
Polyester capacitors use polarized polyester film as the dielectric material and have a positive temperature coefficient, meaning that the capacitance increases as the temperature rises. This is a non-polarized capacitor.
2. Advantages
Polyester capacitors have many advantages, including high temperature resistance, high voltage resistance, and moisture resistance. In addition, they are relatively inexpensive, making them widely used in circuit design.
3. Applications
Polyester capacitors are typically used in mid to low-frequency circuits. Common models include the CL11 and CL21 series. Due to their positive temperature coefficient, they can be used in circuits to automatically compensate for changes in capacitance, thereby improving circuit stability and reliability. Polyester capacitors can also be used in power filtering, demodulation, coupling, and other circuits.
Three, Polystyrene Capacitor (CB)
1. Structure
Polystyrene capacitors come in two types: foil type and metallized type. The foil type polystyrene capacitor has the characteristics of high insulation resistance, low dielectric loss, stable capacity, and high precision, but it has a larger volume and poor heat resistance. The metallized type polystyrene capacitor has better moisture resistance and stability than the foil type, and can self-heal after breakdown, but its insulation resistance is lower and its high frequency characteristics are poor.
2. Advantages
The advantages of polystyrene capacitors are stable capacity, high precision, and suitable for medium and high frequency circuits. The foil type polystyrene capacitor has high insulation resistance and low dielectric loss, while the metallized type polystyrene capacitor has better moisture resistance and stability, and can self-heal after breakdown.
3. Applications
Polystyrene capacitors are commonly used in medium and high frequency circuits. Common models include CB10, CB11 (non-sealed foil type), CB14~16 (precision type), CB24, CB25 (non-sealed metallized type), CB80 (high voltage type), CB40 (sealed metallized type), and other series.
Polypropylene Capacitor (CBB)
1. Structure
Polypropylene capacitors use non-polar polypropylene film as the dielectric, and are a type of negative temperature coefficient non-polar capacitor. They come in two types: non-sealed and sealed. Non-sealed capacitors are often encapsulated with colored resin paint, while sealed capacitors are encapsulated with metal or plastic shells.
2. Advantages
Polypropylene capacitors have the advantages of low loss, stable performance, good insulation, and large capacity.
3. Applications
Polypropylene capacitors are mainly used in middle and low frequency electronic circuits, and can also be used as starting capacitors for motors. Common foil-type polypropylene capacitor models include CBB10, CBB11, CBB60, CBB61, etc., while metallized polypropylene capacitor models include CBB20, CBB21, CBB401, and other series.

Monolithic Ceramic Capacitor
1. Structure
Monolithic ceramic capacitor is a type of ultra-small capacitor with a multi-layered chip structure, made by sintering ceramic materials mainly composed of barium titanate. It consists of multiple electrodes and insulating layers, which are alternately stacked to form a multi-layered structure.
2. Advantages
Monolithic ceramic capacitors have the advantages of reliable performance, high temperature resistance, moisture resistance, large capacitance (capacitance range from 1 pF to 1 μF), and low leakage current. Due to the use of ceramic materials as the dielectric, it has excellent stability and a small temperature coefficient.
3. Disadvantages
The working voltage of monolithic ceramic capacitors is relatively low, generally less than 100 V, so they cannot be used in high-voltage circuits.
4. Applications
Monolithic ceramic capacitors are widely used in resonance, bypass, coupling, filtering, and other circuits. Common series include CT4 (low frequency), CT42 (low frequency), CC4 (high frequency), CC42 (high frequency), etc. In circuits, monolithic ceramic capacitors can be used to achieve high-precision capacitance matching, thereby improving circuit performance and stability. In addition, monolithic ceramic capacitors can also be used in signal processing, communication, radar, antenna, and other fields.
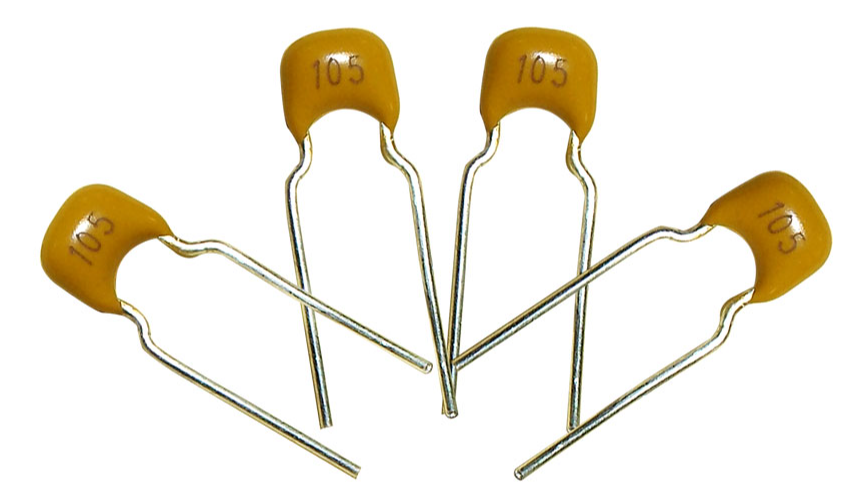

Mica Capacitors(CY)
Mica capacitors, also known as silver mica capacitors, are a type of capacitor that uses mica as its dielectric material and silver as its electrode material. They are widely used in high-frequency circuits for signal coupling, bypassing, and tuning purposes.
1. Structure:
Mica capacitors are made by stacking layers of mica sheets with a thin layer of silver coating on each side. The layers are then compressed and encapsulated in a case made of vulcanized fiber, ceramic, or plastic. The silver coating on the mica sheets acts as the capacitor's electrodes.
2. Advantages:
Mica capacitors have several advantages over other types of capacitors. They offer high stability, low distributed inductance, high precision, low losses, high insulation resistance, good temperature and frequency characteristics, and high operating voltages (ranging from 50 V to 7 kV).
3. Applications:
Mica capacitors are commonly used in high-frequency circuits for signal coupling, bypassing, and tuning purposes. Some of the commonly used series of mica capacitors include CY, CYZ, and CYRX.

Paper Capacitor (CZ)
1. Structure
The paper capacitor uses thin capacitor-specific paper as the dielectric, with aluminum foil or lead foil as the electrode, and is wound, impregnated, and encapsulated.
2. Advantages
The paper capacitor has the advantages of large capacitance (100 pF~100 μF) and wide working voltage range, with a maximum withstand voltage of up to 6.3 kV.
3. Applications
The paper capacitor has a large volume, low capacitance accuracy, high loss, and poor stability. Common series include CZ11, CZ30, CZ31, CZ32, CZ40, CZ80, etc. They are usually used in low-frequency circuits for DC coupling, bypass, filtering, and tuning applications. Paper capacitors are also widely used in some high-end audio equipment.

Metalized Paper Capacitor (CJ)
1. Structure
The metalized paper capacitor is made by using vacuum evaporation technology to deposit a layer of metal film as an electrode on paper coated with varnish.
2. Advantages
Compared to ordinary paper capacitors, metalized paper capacitors have the following advantages:
(1) Small size: Since a metal film is used as an electrode, the volume of the capacitor can be greatly reduced, making it more suitable for use in high-density circuit boards.
(2) Large capacity: The capacitance of metalized paper capacitors is larger than that of ordinary paper capacitors, which can meet the requirements of higher circuit demand.
(3) Strong self-healing ability after breakdown: Metalized paper capacitors can self-heal after breakdown, which will not cause a short circuit in the circuit, thereby improving the stability and reliability of the circuit.

Structure of Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitor (CD)
Polarized aluminum electrolytic capacitors are made by winding aluminum foil (positive electrode) with an oxide film, impregnated with electrolyte, and cathode (negative electrode) foil. The appearance is usually tube-shaped or upright, with a blue or black plastic cover.
1. Advantages
The capacity range of aluminum electrolytic capacitors is large, generally from 1 to 10,000μF, with a rated working voltage range of 6.3V to 450V.
2. Disadvantages
Aluminum electrolytic capacitors have higher dielectric loss and larger capacity error (maximum allowable deviation of +100%, -20%). In addition, their high-temperature resistance is poor, and they are prone to failure after long-term storage.
3. Applications
Aluminum electrolytic capacitors are usually used in DC power circuits or middle and low frequency circuits, playing a role in filtering, decoupling, signal coupling, time constant setting, and DC isolation. It should be noted that they cannot be used in AC power circuits. When used as a filtering capacitor in a DC power supply, the polarity cannot be reversed.

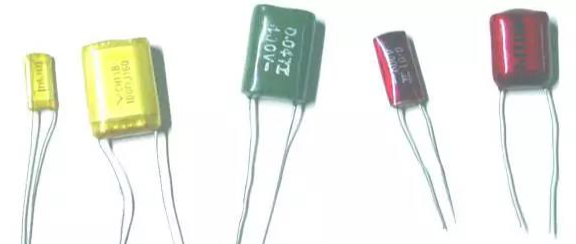
Tantalum Electrolytic Capacitor (CA)
1. Structure
There are two forms of tantalum electrolytic capacitors: 1. Foil-type tantalum electrolytic capacitor, which uses a winding core internally, with the negative electrode being a liquid electrolyte and the dielectric being tantalum oxide. The model numbers include CA30, CA31, CA35, CAk35, and other series; 2. Tantalum powder sintered type, where the anode (positive electrode) is made by pressing and sintering fine tantalum powder. There are various packaging forms, and the model numbers include CA40, CA41, CA42, CA42H, CA49, CA70 (non-polarity), and other series.
2. Advantages
Tantalum electrolytic capacitors have the advantages of low dielectric loss, good frequency characteristics, high temperature resistance, and low leakage current.
3. Disadvantages
The production cost of tantalum electrolytic capacitors is high, and they have low voltage resistance.
4. Applications
Tantalum electrolytic capacitors are widely used in various medium and low-frequency circuits and time constant setting circuits in communication, aerospace, military, and household appliances.
Recent Posts








Company
About UsContact UsTerms & ConditionsPrivacy StatementPayment,Shipping & InvoiceRefund & Return PolicyWarranty PolicyFrequently asked questionHolidays for Chinese Mid-Autumn Festival and National Day in 2023